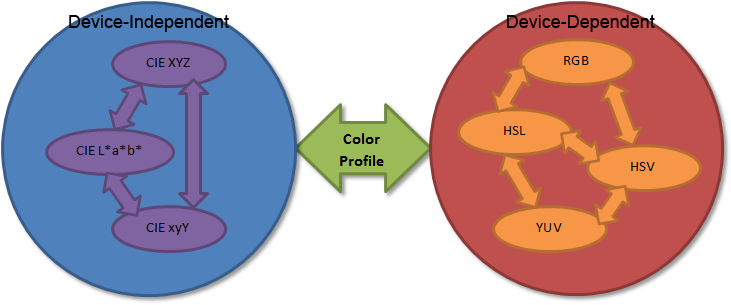
As seen in the Colorimetry page, it's important to understand the difference between Absolute (or device-independent) Color Space (.e.g. CIEXYZ, CIExyY, CIELAB) and device-dependent colors spaces (e.g. RGB, HSL, HSB, HSV).
For example, it makes sense to convert from a device-dependent RGB space to a HSL space since, even though they are both device-dependent, they are defined in the same "dependent space".
Also, it makes sense to convert from 2 device-independent spaces like CIEXYZ and CIELAB.
Most importantly, the conversions between device-dependent color spaces and device-independent color spaces must always be accompanied by a Color Profile that appropriately describes the dependence to the device.
Contents
- 1 Device-Dependent Color Space Conversions
- 2 Device-Independent Color Space Conversions
- 3 Device-dependent / Device-independent Color Space Conversions
- 4 Dealing with Generic Color Profiles
Device-Dependent Color Space Conversions
Here, we will list the different conversions between device-dependent color spaces.
RGB / HSL
(Source: http://www.easyrgb.com)
RGB → HSL
- Input: RGB in [0,1]
- Output: HSL in [0,1]
var_Min = min( R, G, B ) // Min. value of RGB
var_Max = max( R, G, B ) // Max. value of RGB
del_Max = var_Max - var_Min // Delta RGB value
L = ( var_Max + var_Min ) / 2
if ( del_Max == 0 ) // This is a gray, no chroma...
{
H = 0 // HSL results from 0 to 1
S = 0
}
else // Chromatic data...
{
if ( L < 0.5 ) S = del_Max / ( var_Max + var_Min )
else S = del_Max / ( 2 - var_Max - var_Min )
del_R = ( ( ( var_Max - var_R ) / 6 ) + ( del_Max / 2 ) ) / del_Max
del_G = ( ( ( var_Max - var_G ) / 6 ) + ( del_Max / 2 ) ) / del_Max
del_B = ( ( ( var_Max - var_B ) / 6 ) + ( del_Max / 2 ) ) / del_Max
if ( var_R == var_Max ) H = del_B - del_G
else if ( var_G == var_Max ) H = ( 1 / 3 ) + del_R - del_B
else if ( var_B == var_Max ) H = ( 2 / 3 ) + del_G - del_R
if ( H < 0 ) H += 1
if ( H > 1 ) H -= 1
}
HSL → RGB
- Input: HSL in [0,1]
- Output: RGB in [0,1]
if ( S == 0 )
{
(R,G,B) = L;
}
else
{
if ( L < 0.5 ) var_2 = L * ( 1 + S )
else var_2 = ( L + S ) - ( S * L )
var_1 = 2 * L - var_2
R = Hue_2_RGB( var_1, var_2, H + ( 1 / 3 ) )
G = Hue_2_RGB( var_1, var_2, H )
B = Hue_2_RGB( var_1, var_2, H - ( 1 / 3 ) )
}
Hue_2_RGB( v1, v2, vH )
{
if ( vH < 0 ) vH += 1
if ( vH > 1 ) vH -= 1
if ( ( 6 * vH ) < 1 ) return ( v1 + ( v2 - v1 ) * 6 * vH )
if ( ( 2 * vH ) < 1 ) return ( v2 )
if ( ( 3 * vH ) < 2 ) return ( v1 + ( v2 - v1 ) * ( ( 2 / 3 ) - vH ) * 6 )
return ( v1 )
}
RGB / HSV
(Source: http://www.easyrgb.com)
RGB → HSV
- Input: RGB in [0,1]
- Output: HSV in [0,1]
var_Min = min( R, G, B ) // Min. value of RGB
var_Max = max( R, G, B ) // Max. value of RGB
del_Max = var_Max - var_Min // Delta RGB value
V = var_Max
if ( del_Max == 0 ) // This is a gray, no chroma...
{
H = 0 // HSV results from 0 to 1
S = 0
}
else // Chromatic data...
{
S = del_Max / var_Max
del_R = ( ( ( var_Max - var_R ) / 6 ) + ( del_Max / 2 ) ) / del_Max
del_G = ( ( ( var_Max - var_G ) / 6 ) + ( del_Max / 2 ) ) / del_Max
del_B = ( ( ( var_Max - var_B ) / 6 ) + ( del_Max / 2 ) ) / del_Max
if ( var_R == var_Max ) H = del_B - del_G
else if ( var_G == var_Max ) H = ( 1 / 3 ) + del_R - del_B
else if ( var_B == var_Max ) H = ( 2 / 3 ) + del_G - del_R
if ( H < 0 ) H += 1
if ( H > 1 ) H -= 1
}
HSV → RGB
- Input: HSV in [0,1]
- Output: RGB in [0,1]
if ( S == 0 ) // HSV from 0 to 1
{
(R,G,B) = V
}
else
{
var_h = H * 6
if ( var_h == 6 ) var_h = 0 // H must be < 1
var_i = int( var_h ) // Or ... var_i = floor( var_h )
var_1 = V * ( 1 - S )
var_2 = V * ( 1 - S * ( var_h - var_i ) )
var_3 = V * ( 1 - S * ( 1 - ( var_h - var_i ) ) )
if ( var_i == 0 ) { R = V ; G = var_3 ; B = var_1 }
else if ( var_i == 1 ) { R = var_2 ; G = V ; B = var_1 }
else if ( var_i == 2 ) { R = var_1 ; G = V ; B = var_3 }
else if ( var_i == 3 ) { R = var_1 ; G = var_2 ; B = V }
else if ( var_i == 4 ) { R = var_3 ; G = var_1 ; B = V }
else { R = V ; G = var_1 ; B = var_2 }
}
Device-Independent Color Space Conversions
Here, we will list the different conversions between device-independent color spaces.
XYZ / xyY
(Source: http://www.easyrgb.com)
XYZ → xyY
- Input: (Observer. = 2°, Illuminant = D65)
- X in [0, 0.95047]
- Y in [0, 1.00000]
- Z in [0, 1.08883]
- Output: xyY in [0,1]
Y = Y x = X / ( X + Y + Z ) y = Y / ( X + Y + Z )
xyY → XYZ
- Input: xyY in [0,1]
- Output: (Observer. = 2°, Illuminant = D65)
- X in [0, 0.95047]
- Y in [0, 1.00000]
- Z in [0, 1.08883]
X = x * ( Y / y ) Y = Y Z = ( 1 - x - y ) * ( Y / y )
XYZ / Lab
(Source: http://www.easyrgb.com)
Remember that CIE L*a*b* is device-independent but needs a white point reference nevertheless.
Here, the D65 illuminant is used.
XYZ → L*a*b*
- Input: (Observer. = 2°, Illuminant = D65)
- X in [0, 0.95047]
- Y in [0, 1.00000]
- Z in [0, 1.08883]
- Output:
- L* in [0,100]
- a*, b* in [-1,1]
var_X = X / ref_X // ref_X = 0.95047 Observer= 2°, Illuminant= D65 var_Y = Y / ref_Y // ref_Y = 1.000 var_Z = Z / ref_Z // ref_Z = 1.08883 if ( var_X > 0.008856 ) var_X = var_X ^ ( 1/3 ) else var_X = ( 7.787 * var_X ) + ( 16 / 116 ) if ( var_Y > 0.008856 ) var_Y = var_Y ^ ( 1/3 ) else var_Y = ( 7.787 * var_Y ) + ( 16 / 116 ) if ( var_Z > 0.008856 ) var_Z = var_Z ^ ( 1/3 ) else var_Z = ( 7.787 * var_Z ) + ( 16 / 116 ) CIE-L* = ( 116 * var_Y ) - 16 CIE-a* = 500 * ( var_X - var_Y ) CIE-b* = 200 * ( var_Y - var_Z )
L*a*b* → XYZ
- Input:
- L* in [0,100]
- a*, b* in [-1,1]
- Output: (Observer. = 2°, Illuminant = D65)
- X in [0, 0.95047]
- Y in [0, 1.00000]
- Z in [0, 1.08883]
var_Y = ( CIE-L* + 16 ) / 116 var_X = CIE-a* / 500 + var_Y var_Z = var_Y - CIE-b* / 200 if ( var_Y^3 > 0.008856 ) var_Y = var_Y^3 else var_Y = ( var_Y - 16 / 116 ) / 7.787 if ( var_X^3 > 0.008856 ) var_X = var_X^3 else var_X = ( var_X - 16 / 116 ) / 7.787 if ( var_Z^3 > 0.008856 ) var_Z = var_Z^3 else var_Z = ( var_Z - 16 / 116 ) / 7.787 X = ref_X * var_X // ref_X = 0.95047 Observer= 2°, Illuminant= D65 Y = ref_Y * var_Y // ref_Y = 1.00000 Z = ref_Z * var_Z // ref_Z = 1.08883
Device-dependent / Device-independent Color Space Conversions
RGB (in sRGB) / XYZ
(Source: http://www.easyrgb.com)
Please refer to the sRGB color profile specification to understand the pseudo-gamma correction in the following routines.
RGB → XYZ
- Input: RGB in [0,1] with sRGB gamma profile
- Output: (Observer. = 2°, Illuminant = D65)
- X in [0, 0.95047]
- Y in [0, 1.00000]
- Z in [0, 1.08883]
// Apply gamma correction (i.e. conversion to linear-space) if ( R > 0.04045 ) R = ( ( R + 0.055 ) / 1.055 ) ^ 2.4 else R = R / 12.92 if ( G > 0.04045 ) G = ( ( G + 0.055 ) / 1.055 ) ^ 2.4 else G = G / 12.92 if ( B > 0.04045 ) B = ( ( B + 0.055 ) / 1.055 ) ^ 2.4 else B = B / 12.92 // Observer. = 2°, Illuminant = D65 X = R * 0.4124 + G * 0.3576 + B * 0.1805 Y = R * 0.2126 + G * 0.7152 + B * 0.0722 Z = R * 0.0193 + G * 0.1192 + B * 0.9505
XYZ → RGB
- Input: (Observer. = 2°, Illuminant = D65)
- X in [0, 0.95047]
- Y in [0, 1.00000]
- Z in [0, 1.08883]
- Output: RGB in [0,1] with sRGB gamma profile
R = X * 3.2406 + Y * -1.5372 + Z * -0.4986 G = X * -0.9689 + Y * 1.8758 + Z * 0.0415 B = X * 0.0557 + Y * -0.2040 + Z * 1.0570 if ( R > 0.0031308 ) R = 1.055 * ( R ^ ( 1 / 2.4 ) ) - 0.055 else R = 12.92 * R if ( G > 0.0031308 ) G = 1.055 * ( G ^ ( 1 / 2.4 ) ) - 0.055 else G = 12.92 * G if ( B > 0.0031308 ) B = 1.055 * ( B ^ ( 1 / 2.4 ) ) - 0.055 else B = 12.92 * B
RGB (in Adobe RGB) / XYZ
(Source: http://www.adobe.com/digitalimag/pdfs/AdobeRGB1998.pdf)
RGB → XYZ
- Input: RGB in [0,1] with Adobe RGB gamma profile
- Output: (Observer. = 2°, Illuminant = D65)
- X in [0, 0.95047]
- Y in [0, 1.00000]
- Z in [0, 1.08883]
// Gamma correction of ~2.2 R = R ^ 2.19921875 G = G ^ 2.19921875 B = B ^ 2.19921875 // Observer. = 2°, Illuminant = D65 X = 0.57667 * R + 0.18556 * G + 0.18823 * B Y = 0.29734 * R + 0.62736 * G + 0.07529 * B Z = 0.02703 * R + 0.07069 * G + 0.99134 * B
XYZ → RGB
- Input: (Observer. = 2°, Illuminant = D65)
- X in [0, 0.95047]
- Y in [0, 1.00000]
- Z in [0, 1.08883]
- Output: RGB in [0,1] with Adobe RGB gamma profile
R = 2.04159 * X - 0.56501 * Y - 0.34473 * Z G = -0.96924 * X + 1.87597 * Y + 0.04156 * Z B = 0.01344 * X - 0.11836 * Y + 1.01517 * Z // Gamma correction R = R ^ (1.0 / 2.19921875) G = G ^ (1.0 / 2.19921875) B = B ^ (1.0 / 2.19921875)
RGB (in Adobe RGB ICC Profile v2.4) / XYZ
(Source: http://www.adobe.com/digitalimag/pdfs/AdobeRGB1998.pdf)
RGB → XYZ
- Input: RGB in [0,1] with Adobe RGB gamma profile
- Output: (Observer. = 2°, Illuminant = D50)
- X in [0, 0.9642]
- Y in [0, 1.0000]
- Z in [0, 0.8249]
// Gamma correction of ~2.2 R = R ^ 2.19921875 G = G ^ 2.19921875 B = B ^ 2.19921875 // Observer. = 2°, Illuminant = D50 X = 0.60974 * R + 0.20528 * G + 0.14919 * B Y = 0.31111 * R + 0.62567 * G + 0.06322 * B Z = 0.01947 * R + 0.06087 * G + 0.74457 * B
XYZ → RGB
- Input: (Observer. = 2°, Illuminant = D50)
- X in [0, 0.9642]
- Y in [0, 1.0000]
- Z in [0, 0.8249]
- Output: RGB in [0,1] with Adobe RGB gamma profile
R = 1.96253 * X - 0.61068 * Y - 0.34137 * Z G = -0.97876 * X + 1.91615 * Y + 0.03342 * Z B = 0.02869 * X - 0.14067 * Y + 1.34926 * Z // Gamma correction R = R ^ (1.0 / 2.19921875) G = G ^ (1.0 / 2.19921875) B = B ^ (1.0 / 2.19921875)
RGB (in ProPhoto RGB) / XYZ
(Source: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.202.294)
RGB → XYZ
- Input: RGB in [0,1] with ProPhoto RGB gamma profile
- Output: (Observer. = 2°, Illuminant = D50)
- X in [0, 0.96421]
- Y in [0, 1.00000]
- Z in [0, 0.82519]
// Gamma correction if ( R > 16 * 0.001953 ) R = R ^ 1.8 else R = R / 16 if ( G > 16 * 0.001953 ) G = G ^ 1.8 else G = G / 16 if ( B > 16 * 0.001953 ) B = B ^ 1.8 else B = B / 16 // Observer. = 2°, Illuminant = D50 X = 0.7977 * R + 0.1352 * G + 0.0313 * B Y = 0.2880 * R + 0.7119 * G + 0.0001 * B Z = 0.0000 * R + 0.0000 * G + 0.8249 * B
XYZ → RGB
- Input: (Observer. = 2°, Illuminant = D50)
- X in [0, 0.96421]
- Y in [0, 1.00000]
- Z in [0, 0.82519]
- Output: RGB in [0,1] with ProPhoto RGB gamma profile
R = 1.3460 * X - 0.2556 * Y - 0.0511 * Z G = -0.5446 * X + 1.5082 * Y + 0.0205 * Z B = 0.0000 * X + 0.0000 * Y + 1.2123 * Z // Gamma correction if ( R > 0.001953 ) R = R ^ ( 1 / 1.8 ) else R = 16.0 * R if ( G > 0.001953 ) G = G ^ ( 1 / 1.8 ) else G = 16.0 * G if ( B > 0.001953 ) B = B ^ ( 1 / 1.8 ) else B = 16.0 * B
RGB (in Radiance RGB) / XYZ
Radiance RGB is the default profile for Radiance files (*.HDR) and the chromaticities found in the source code are:
| color | x | y |
|---|---|---|
| Red | 0.64 | 0.33 |
| Green | 0.29 | 0.6 |
| Blue | 0.15 | 0.06 |
| White | 0.3333 | 0.3333 |
RGB → XYZ
- Input: RGB in [0,1]
- Output:
- X in [0, 0.96421]
- Y in [0, 1.00000]
- Z in [0, 0.82519]
X = 0.5141 * R + 0.3238 * G + 0.1619 * B Y = 0.2651 * R + 0.6701 * G + 0.0647 * B Z = 0.0241 * R + 0.1228 * G + 0.8530 * B
XYZ → RGB
- Input:
- X in [0, 0.96421]
- Y in [0, 1.00000]
- Z in [0, 0.82519]
- Output: RGB in [0,1]
R = 2.5653 * X - 1.1668 * Y - 0.3984 * Z G = -1.0221 * X + 1.9783 * Y + 0.0438 * Z B = 0.0747 * X - 0.2519 * Y + 1.1772 * Z
Dealing with Generic Color Profiles
XYZ Matrices
When dealing with standard profiles like sRGB, Adobe RGB or ProPhoto RGB you are given the chromaticities of Red, Green, Blue and the one for the White Point.
Also, when opening PNG file you can encounter the cHRM chunk that describes the same chromaticities. You then need to transform these 4 2D values into a 3x3 matrix to convert the RGB value to and from the XYZ master space.
First of all, remembering our basic CIEXYZ and CIExyY conversions, let's enumerate what we know:
- <math>xyz_R = \frac{XYZ_R}{X_R+Y_R+Z_R} = \frac{XYZ_R}{\Sigma_R}</math> from the chromaticities for Red
- <math>xyz_G = \frac{XYZ_G}{X_G+Y_G+Z_G} = \frac{XYZ_G}{\Sigma_G}</math> from the chromaticities for Green
- <math>xyz_B = \frac{XYZ_B}{X_B+Y_B+Z_B} = \frac{XYZ_B}{\Sigma_B}</math> from the chromaticities for Blue
- <math>xyz_W</math> from the chromaticities for White
- <math>Y_W = 1</math> standard luminance for White
- <math>XYZ_W</math> (since we have a completely defined <math>xyY_W</math>, we can thus easily convert to <math>XYZ_W</math>, see CIE XYZ color space)
Note that we don't know the <math>XYZ_R</math>, <math>XYZ_G</math> and <math>XYZ_B</math> vectors.
So we are looking for <math>M_{XYZ}</math> so that:
- <math>
XYZ = RGB . M_{XYZ} = RGB . \begin{bmatrix} XYZ_R \\ XYZ_G \\ XYZ_B \end{bmatrix} = RGB . \begin{bmatrix} \Sigma_R.xyz_R \\ \Sigma_G.xyz_G \\ \Sigma_B.xyz_B \end{bmatrix} </math>
Using <math>RGB_W = [1,1,1]</math> we can write:
- <math>XYZ_W = [1,1,1] . M_{XYZ} = \Sigma_R.xyz_R + \Sigma_G.xyz_G + \Sigma_B.xyz_B</math>
Or, in matrix form again:
- <math>XYZ_W = \Sigma_{RGB} .
\begin{bmatrix} xyz_R \\ xyz_G \\ xyz_B \end{bmatrix} = \Sigma_{RGB} . M_{xyz} </math>
Solving by right composing with <math>M_{xyz}^{-1}</math>:
- <math>
\Sigma_{RGB} = XYZ_W . M_{xyz}^{-1} </math>
we thus obtain <math>\Sigma_{RGB}</math> and since:
- <math>
\begin{bmatrix} \Sigma_R . xyz_R \\ \Sigma_G . xyz_G \\ \Sigma_B . xyz_B \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} XYZ_R \\ XYZ_G \\ XYZ_B \end{bmatrix} = M_{XYZ} </math>
we finally obtain <math>M_{XYZ}</math> that converts a RGB color into an XYZ color (obviously, you need to use the inverse <math>M_{XYZ}^{-1}</math> to convert from XYZ back into RGB).
Custom ICC Profiles
Decoding true ICC profiles is a little over the top for our purpose so I won't be discussing full custom profiles here although you can read the ICC Profile specs if you like.
Also, if you really need a complete CMS, you should download the excellent Little CMS by Marti Maria.